- to carry water from one reservoir to another reservoir seperated by a hill or ridge.
- to take out the liquid from tank which is not having any outlet.
- to empty a channel not provided with any outlet sluice.
Syphon
Labels: Hydraulic Machine
Methods for finding different Part family
1.Visual Inspection
It is the least sphosticated and least expensive method. It involves classification of parts into family by looking either the physical parts or photograghs and arranging them into similar group.
2.Production flow analysis (PFA)
It is a method of identifying part family and associated machine tool grouping by analysing the route sheet (process planning) for parts produced in a given machine shop. It groups together the parts that have similar operation sequence and machine routings. The disadvantages is it blindly accept the excisting route sheet without considering whether they are logical or consistent.
3.Parts Classification and Coding
We are considering both the design and manufacturing attitudes of each Parts.
Design Attitudes:-basic internal shape and external shape,Length of dia. ratio,material type,tolerance
Manufacturing Attitudes:-major process,minor process,batch size,machine tool used,surface finish
Labels: CAD/CAM
Part Family -Definition
It is a collection of parts which are similar either because of design attitude or manufaturing attitudes. The parts within the family are different but their similarities areclose enough to put them under the same part family.
Labels: CAD/CAM
AUTOMATED PROCESS PLANNING
Group Technology(GT)
It is manufacturing phylosphy similar parts are identified and grouped together to take their advantages of their similarity in manufacturing and design.
Parts Classfication and Coding
It is concern with identifying the similarities and relating this similarities to a coding system. Two types
- Design Attributes:-Such as geometrical shape and size
- Manufaturing Attributes:-Such as sequence of processing step required to make the part.
Labels: CAD/CAM
Program to reverse any number
14. Write a program to reverse any number?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int n,d r=0;
clrscr()
printf("enter the no");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n>0)
{
d=n%10;
r=(r*10)+d;
n=n/10;
}
printf("reverse %d",r);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read the number n,d,r
3.calculate d=n%10
r=(r*10)+d
n=n/10
4.print r
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter 234
432
Labels: C-program
Evaluate Y=Xˆn
13. write a program to evaluate Y=Xˆn?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int Y=1,X,n,i=i;
clrscr();
printf("enter two numbers");
scanf("%d%d",&X&n);
while(i<=n)
{
Y=Y*X;
i++;
}
printf("%d',Y);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.enter the values of X and n
3.check
4.calculate Y=Y*i
5.print the value of Y
6.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
Enter the two numbers 4 4
256
Labels: C-program
Find the factorial of a number
12.Write a program to find the factorial of a number?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int n,f=1,i=i;
clrscr();
printf("enter the no.");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(i<=n)
{
f=f*i;
i++;
}
printf("%d",f);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read n
3.calculate f=f*i
4.print factorial
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
Enter 2
2
Labels: C-program
find the sum of first ten natural numbers
11. Write a program to find the sum of first ten natural numbers?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int i=1,sum=o;
clrscr();
while(i<=10)
{
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}
printf("sum is %d", sum);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.check the number is less than or equal to 10
3.calculate the sum of 10 natural numbers
4.print sum
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
55
Labels: C-program
find the largest among three numbers
10. Write a program find the largest among three numbers?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int a,b,c;
clrscr();
printf(" enter three nos.");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
if((a>b)&&(a>c)
printf("large%d",a);
else
if((b>c)&&(b>c))
printf("large%d",b);
else
printf("large%d',c);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a,b,c
3.if (a>b)&(a>c)
4.print large is a
5.else
6.if (b>c)&(b>a)
7.print large is b
6.else
7.print large is c
8.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired is obtained
Output
enter three numbers
1 3 5
large 5
Labels: C-program
find the largest of given two numbers
9. Write a Program to find the largest of given numbers?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("enter the numbers");
scanf(%d%d",&a,&b);
if(a>b)
printf("large %d ",a);
else
printf("small %d", a);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a,b
3.if (a>b)
4.print large
5.else
6.print small
7.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter numbers
2 4
large 4
Labels: C-program
Check the number is a happy number
8. Write a program to find the number is a happy number?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int a,r1,r2,b,x,r3,r4;
clrscr();
printf("enter the number");
scanf("%d",&a);
x=a;
r1=a%10;
r2=a%100;
r3=(r2-r1)/10;
r4=(a-r2)/100;
b=(r1*r1*r1)+(r3*r3*r3)+(r4*r4*r4);
if(b==x)
printf("happy number");
else
printf("not");
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a
3.calculate
r1=a%10
r2=a%100
r3=(r2-r1)/10
r4=(a-r2)/100
b=r1³+r3³+r4³
5.if b=x
6.print happy no
7.else
8.print not
9.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully excecuted and desired output is obtained.
Output
enter the no.
153
happy no
Labels: C-program
The given number is positive or not
7. write a Program to find the given number is positive or not?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int a;
clrscr();
printf("enter the number");
scanf('%d",&a);
if(a>0)
{
printf("no is Positive");
}
printf("no. is not positive");
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a
3. if a>0
4.print no. is +ive
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained.
Output
Enter the number
2
no. is +ive
Labels: C-program
Definitions
1. Periodic motion –A motion which repeats itself after equal intervals of time is known as periodic motion. Any periodic can be represented by function x(t) in the period T, the function x(t) is called periodic function
2. Time Period – Time taken to complete one cycle is called periodic function.
3. Frequency –The number of cycles per unit time is known as frequency
4. Natural frequency – When no external force acts on the system after giving it an initial displacement , the body vibrates. These vibration are called free vibrations and their frequency as natural frequency. It is expressed in c/s or hertz
5. Amplitude – The max displacement of a vibrating body from its equilibrium position is called amplitude
6. Fundamental mode of vibration – The fundamental mode of vibration of a system is the mode having the lowest natural frequency
7. Resonance – When the frequency of external exitation is equal to the natural frequency of a vibrating body, the amplitude of vibration becomes excessively large. This concept is known as resonace
8. Mechanical System – The system consisting of mass shiftness and damping are known as mechanical system.
9. Continuous and Discrete system – Most of mechanical system include elastic members which have infinite number of degree of freedom. Such system are called continuous system or distributed system. Eg. Cantilever,Simply Supported beam System with finite number of degrees of freedom are called discrete system
10. Degree of freedom – The minimum no. of independent co-ordinates required to specify the motion of a system at any instant is known as degree of freedom of the system
11. Simple harmonic motion – A periodic motion of a particle whose acceleration is always directed towards the mean position and is proportional to its distance from the mean position is known as SHM. It may also defined as the motion of a projection of a particle moving round a circle with uniform angular velocity on a diameter.
12. Phase difference – the angle between two rotating vectors representing simple harmonic motion of the same frequency
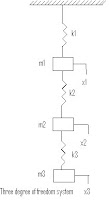
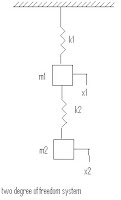
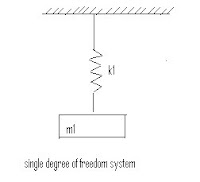
Labels: Dynamics of Machine (DOM)
Mechanical Vibration
The study of vibration is concerned with the oscillatory motion of bodies and the forces associated with them. All bodies possessing mass and elasticity are capable of vibrating. Thus most engineering machines and structures experiences vibration to some degree. Undesirable vibration in machines may cause the loosening of parts
Cause of vibration
1. Unbalanced forces –within machine itself,non-uniform material distribution
2. Dry friction between the two mating surfaces
3. External Excitation
4. Elastic nature of the system
5. Earth Quakes
6. Winds
Effect of vibration
• Excessive stress
• Undesirable noise
• Loosening of parts
• Partial or complete failure of parts
Uses
• Musical instruments
• Vibrating screen
• Shakers
• Stress relieving
Methods to reduce vibration
1. Removing the cause of vibration
2. Putting in screens if noise is the only objection
3. Resting the machinery in proper type of isolators
4. Shock Absorbers
5. Dynamic vibration absorber
Labels: Dynamics of Machine (DOM)
Types of Damping
Viscous Damping
It is encountered by bodies moving at moderate speed through liquid. This type of damping leads to a resisting force proportional to the velocity. The damping force
Fd ∞ dx/dt
Fd =cx
‘c’ is the constant of proportionality and is called viscous damping Co-eff. With the dimension of N-S/m
Colomb Damping
This type of damping arises from sliding of dry surfaces.The friction force is nearly constant and depends upon the nature of sliding surface and normal pressure between them as expressed by the equation of kinetic friction
F = µN
Where µ =co-eff of friction
N = normal force
Solid or structural Damping
This is due to internal friction within the material itself.Experiment indicates that the solid damping differs from viscous damping in that it is independent of frequency and proportional to maximum stress of vibration cycle.
Slip or Intrefacial damping
Energy of vibration is dissipated by microscopic slip on the interfaces of machine parts in contact under fluctuating loads. Microscopic slip also occurs on the interface of the machine elements having various types of joints. This type is essentially of a linear type.
Labels: Dynamics of Machine (DOM)
Check the number is odd or not
6.Write a program to check whether the number is odd or even?
#include
#include
void main ()
{
int a;
clrscr();
printf("enter the no.");
scanf("%d",&a);
if(a%2==0)
printf("no. is even %d",a);
else
printf("odd");
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a
3.if (a%2=0)
4.print even
5.else
6.print odd
7.stop
Result
The program was sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter the no
4
even
Labels: C-program
Reverse of a three digit number
5.Write a program to reverse a three digit number?
#include
#include
void main()
{
int a,r1,r2,b,c,rev;
clrscr();
printf("enter the no.");
scanf("%d",&a);
r1=a%10;
b=a/10;
r2=b%10;
c=b/10;
rev=(r1*100)+(r2*10)+c;
printf("reverse %d",rev);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a
3.calculate
r1=a%10
b=a/10
r2=b/10
c=b/10
rev=(r1*100)+(r2*10)+c
4.print rev
5.stop
Result
The program was sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter the no.
123
reverse is 321
Labels: C-program
Sum of digits of a three digit number
4.Write a program to find the sum of digits of a three digit number?
#include
#include
{
int a,r1,r2,rt,s;
clrscr();
printf("enter the number");
scanf("%d",&a);
r1=a%10;
r2=a%100;
rt=(r2-r1)/10;
r3=(a-r2)/100;
s=r1+rt+r3;
Printf("sum is %d",s);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read a
3.calculate
r1=a%10
r2=a%100
rt=(r2-r1)/10
r3=(a-r2)/100
s=r1+rt+r3
4.print s
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter the no
153
result is 9
Labels: C-program
Area of a circle
3.Write a program to find the area of a circle?
#include
#include
{
int r;
float a, area;
clrscr();
a=3.14;
printf("enter no.");
scanf(%d",&r);
area=a*r*r;
printf("result is %f",area);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read radius r and a
3.calculate area =a*r*r
4.print area
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and desired output is obtained
Output
enter r
2
result =12.56
Labels: C-program
Average of three numbers
2.Write a program to find the average of three numbers?
#include
#include
{
float a,b,c,avg;
clrscr();
printf("enter three numbers");
scanf("%f%f%f",&a,&b,&c);
avg=(a+b+c)/3;
printf("result is %f",avg);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read three numbers a b c
3.calculate avg =a+b+c/3
4.print avg
5.stop
Result
The program is sucessfully executed and the desired output is obtained.
Output
enter three nos.
2 4 6
result is 4
Labels: C-program
Add two numbers
1.Write a program to add two numbers?
#include
#include
{
int a,b,sum;
clrscr();
printf("enter the no.");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
sum=a+b;
printf("result is %d",sum);
getch();
}
Algorithum
1.start
2.read two numbers a and b
3.calculate the sum =a + b
4.Print sum
5.stop
Result
Thus the program is sucessfully executed and the desired output is obtained.
output
enter the no.
1 2
result =3
Labels: C-program
Vernier Bevel Protractor
 pls click on fig. to be clear
pls click on fig. to be clear
Simplest angle measuring instrument.It consisit of :
i. Main Body
ii. base plate stock
iii.Adjustable blade
iv.Circular plate containing vernier scale
v. acute angle attachment
Above fig shows the Vernier Bevel Protractor with acute angle attachment.The body is designed in such a way that its back is flat and there are no projection beyond its back.The flatness of the body is tested by checking the squareness of blade with respect to base plate (blade at 90 degree)
the base plate is attached to the main body, and an adjustable blade is attachedto a circular plate containing vernier scale. The adjustable blade is capable of rotating freely about the centre of the main scale engraved on the body of the instrument can be locked in any position.The base of the base plate is made flat so that it could be laid flat upon work.Blade can move through its length and reversed. It is 150 or 300mm long,13mm width and 2mm thick.
bevel protractor are tested for flatness,Squareness,parallelism,straightness,etc.
Labels: Metrology
Angular Measurments
Angular Measurments are frequently necessary for the manufacture of interchangeable parts The ships and aeroplanes can navigate confidently without the help of the sight of the land, only because of precise angular measurement.
Angle Standards
In angular measurement , the end standard takes the form of either angle gauges or polygon with the angle defined between adjacent faces. While the line standard takes the form of uniformly defined circles with the lines engraved at regular intervals of say one degree.
Labels: Metrology
Applications of Robots
1. Material Transfer
The robot is used to move the work part from one location to another it includes
a. pick and place operation
b. transfer of work parts from one conveyor to another
c. palletizing and depalletizing
2. Machine loading and unloading
In this robot is used for loading a work part to a production machine and after machining it is unloader.
eg. Die casting - unloader part from die
Hot Forging - loaded the hot billet into the die, hold it during the process and then remove
injection moulding, press working,etc.
3. Welding
a. Spotwelding - Robots helps to position the welding gun at correct location, squeeze the two electrode against welding parts,weld and hold the workpiece,release the tool
b. Arc welding - Contouring robots are used for are welding
- high productivity
- improve safety
- high quality weld
4. Spray Painting
Since spray painting is hazards to human being we are using robots.
- high quality coating
- lower material usage
5. Processing Stations Coperation
It is done by collection the tool to the robot's wrist as end effector,drilling, riveting, grinding,polishing can be done using robot.
6. Assembling and Inspections
Robots can used for assembly and inspection is also hundred percent. Mechanical prop.,optical sensor, used for inspection.
- PUMA assembly
Labels: CAD/CAM
Robot Programming Languages
I .VAL(Victors Assembly Language)
It is developed for robots called PUMA
(a) MONIT commands
It is a set of administrative instructions that direct the operation of robot system
The functions are
- Preparing the system for user to write the program
- defining the points in space.
- Command the PUMA to execute the program
eg. EDIT,EXECUTE,SPEED, HERE
EDIT - used to create or modify the program
EXECUTE- to execute the program
SPEED- controlling the speed
HERE-to define the current position of robot
(b) Program Instruction
Program instruction are entered into the memory to form program by using the MONIT command EDIT, this prepare the system to receive program instruction statement in a proper order.
eg. MOVE - moves the robot to a specified location
DEPART- moves the tool the distance given along the current z-axis
OPEN -to open or close the gripper
EXIT - to exit
II.MCL(Machine Control Language)
It is based on NC language but it is beside to control a complete manufacturing cell. including a cell with robot.MCL is a enhancement of APT which posses additional option and features needed to do the offline programming of work cell
Application
Vision,inspection,control using this programming-commands
DEVICE-to activate a device in the workcell
SEND-to cause an output signal to reach a definite destination
RECEIVE- it cause as input signal to be accepted from a defined source
TASK- allow program to define a certain portion program as a task
Labels: CAD/CAM
Robot Programming
1.Manual Method
It is a procedure used for simpler robots and it involves the setting of mechanical stops,cams etc .in robots control unit and pick place operation robot follows this method.
2.Walk through Method
The programmer manually moves the robot arm and hand through the motion sequence of work cycle Each movements is recorded into the memory for the subsequent play back during the production. The speed can be controlled independently. The programmer does not have worry about cycle time during the walk through method.
eg. used for spray painting, arc welding, etc.
3.Lead Through method
A teach pendant to power drive the robot through its motion sequence. teach pendant is usually a small hand held device with switch and dial to control robot's physical movements. Here also each motion is recorded into the memory.
4.OFF- line Programming
It is similar to NC part programming. a program is prepared and its is stored into the robot memory for the machining during a work cycle.The advantage is time lost due to the teaching of robot is avoided and we can use the service of CAD/CAM system for the advance operation
Labels: CAD/CAM
Evolution of Industrial Engineering
Though F.W.Taylor is named as the father of scientific managment and industrial engineering.
1. 1732 - James Ark Wright - invented the spinning Frames
Which has improved the productivity and quality (British Cotton Textile Industry)
2. 1769 - James Watt -developed Steam Engine
Thus steam engine power brought revolution in industries in terms of useful replacement of manpower by steam power
3. 1776 - Adam Smith - wealth of nations
Introduced concept of division of labour
4. 1772-1891 - Charles Babbage- the economy of machine and manufacturing
Concept -"The Economy of Machinery and Manufacturing " he also reffered the relation and conflicts between labour and management.
5. 1900 - F.W. Taylor- Scientific approach
Scientific approach to managament could improve labour efficency and productivity.he analysis the basic work content of a task and he redesign the task after eliminating the unproductive elements in order to improve the efficency .Relationship of executives and workers and participation of workers in decisison making.
I . Develop a standarised method for doing a job
II . Eliminating waste
III. Wage incentives payment system
IV . Scientific Selection
V . Develop greater understanding between managers and workers
VI . divide work between managament and labour
6. 1900 - Gilberth - MicroMotion study- Therbligs
Principal contribution was identification,analysis and measurement of fundamental motions involved in performing a task. He developed the micro motion study,i.e the subdivision of motion involved in the task.he develops Concept of fatigue in work, and efficency in work-methods
7. 1901 - Henry Gantt- Gantt chart
main application solve scheduling problems. In different forms provide a Systematic Graphical Procedure for Planning ans Scheduling various activies, Reviewing Progress and to Update the Schedules
8. 1913 - Harrington Emerson - principles of efficency
I . Clearly defined ideas
II . Common sense
III. Competent counsel
IV . Displine
V . Fair deal
VI . Reliable,immediate and adequate records
VII.Dispaching
VIII.Standards and Schedules
IX .Efficieny rewards
9. 1915 - F.W.Harris- inventory control
established an optimized technique in inventory economics
10. 1931 - Walter A.Schewhart - statistics in Production
Concept of quality control , inspection, sampling plans
11. 1935 - H.F.Dodge and H.G.Roming
economics of inspection, Stastical sampling to Quality control, Samling Plans.
12. 1937 - L.H.C. Tippet-developed working sampling to study the pattern of work
determine the equipment and manpower utilisation and for selling performance standards for long cycle, hetrogenous jobs.
13. 1940 - P.M.S.Blacket -concept of optimisation,called O.R
14. 1947 - George b. Dantzing
mathematical programming , non linear Programming
15. A.Charles,W.W.Cooper-programming
16. 1955 - I.B.M-Digital Computer
17. 1960 - L.Cumming and L.Poter
organisational Behaviour,study people at work,integartion of man and machine etc.
18. 1970 - Simulation
of production problems, automation,Human Enigneering, Simulation of entire production systems,Automation of Factory, Unmanned Factory
Labels: Industrial Engineering
Co-efficient of Performance (c.o.p)
It is defined as the ratio of heat extracted in the refrigerator to the work done one the refrigerant
Theo. C.O.P =Q/W
Q= Amount of heat extracted in the refrigerator
W=Amount of work done
Relative C.O.P =actual c.o.p/theo. c.o.p
Problem 1.
1.Find the C.O.P of a refrigerator system if work input is 80KJ/Kg and the refrigeration effect produced is 160KJ/Kg of refrigerant flowing ?
Ans.
C.O.P =Q/W ( Q=160KJ/Kg)
=160/80 (W=80KJ/Kg)
=2KJ/Kg
Refrigeration
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is defined as the process of removing heat from a substance under controlled condition or it means a continous extraction of heat from a body whose temperature is already below the temperature of surroundings.
Unit of Refrigeration
Practical Unit of refrigeration is expressed in terms of tonne of refrigeration (TR)
Which is defined as the amount of refrigeration effect produced by the uniform melting of 1 tonne of ice from and at 0 degree celcius in 24 hours.
latent heat of ice =335 KJ/Kg
1TR =1000*335/(24*60)
=232.6 KJ/min
In actual practice 1 tonne of ice is taken as equalent to 210 KJ/min or 3.5KW or KJ/s
Definition and Concept of Metrology
Metrology is a science of measurement.Metrology may be divided depending upon the quantity under consideration into: Metrology of length,metrology of time etc.Depending upon the field of application -industrial metrology and Medical metrology etc.
Engineering metrology is restricted to the measurement of length,angles and other quantities which expressed in linear or angular terms.
In a border sense metrology is not limited to length and angle measurement but also concerned with numerous problems theoretical as well as practical related with measurement such as
1. units of measurement and their standards
2. Methods of measurement based on agreed units and standards.
3. Errors of measurement
4. measuring instruments and devices
5. Accuracy of measuring instruments and their care
6. Industrial inspection
7. Design, manufacturing and testing of gauges of all kinds
Labels: Metrology
Definition and Concept of Industrial Engineering
Industrial Engineering is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated system of people, material,equipment and energy.it draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical,physical and science together with the principles and methods of engineering analysis and design to specify, predict and evaluate the result to be obtained from such system.(defined by A.I.I.E)
I.E is an engineering approach to the detailed analysis and design of the optimum utilization of men, material,money, machine, equipment,and energy i.e the main resources of an organization. The industrial Engineer carries out such analysis in order to achieve the objectives i.e to increase productivity of the organization by uitilising the resources effectively and efficiently.Essentially the Industrial Engineer is engaged in the design of a system and his function is primarily that of management.
The market is facing with severe competition, in almost every sector. The expectation of the customers are increasing day to day and manufactures are struggling to design and produce goods in as much variety as possible to cater to the demands of the new generation customers.Thus there is a challange before the industries to manufacture goods of right quality, and quantity, at right time ,and at minimum cost for their growth survival and even survivalthis demands increase in productvity of the organisation. Industrial Enigneering is going to play an important role in increasing the productivity.
Productivity Improvement Implies
1.more efficient utilization of resources such as men,materials,machine, money, energy.
2.less wastage in production.
3.Maximum output with minimum input at desired quality
Labels: Industrial Engineering










